 Kawasaki Z1000SX - Service manual > Parts Location
Kawasaki Z1000SX - Service manual > Parts Location
- Timing Rotor
- Crankshaft Sensor
- Oxygen Sensor (Equipped Models)

- Horn
- Turn Signal Relay

- Relay Box
- ECU

- Rear Brake Light Switch

- Regulator/Rectifier

- Water Temperature Sensor
- Speed Sensor
- Alternator
- Stator Coil
- Radiator Fan Motor

- Neutral Switch
- Oil Pressure Switch
- Sidestand Switch

- Fuse Boxes
- Battery 12 V 8 Ah
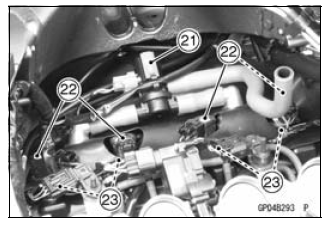
- Starter Relay

- Air Switching Valve
- Stick Coils
- Spark Plugs
- Immobilizer Amplifier (Immobilizer Models)

- Starter Lockout Switch
- Ignition Switch (Immobilizer Model: Including Immobilizer Antenna)
- Meter Unit
- Front Brake Light Switch

Wiring Diagram (US, CA and CAL Models)


Wiring Diagram (Other than US, CA and CAL Models)


Wiring Diagram (CA with ABS Models)


Wiring Diagram (Other than CA with ABS Models)


Precautions
There are a number of important precautions that are musts when servicing electrical systems. Learn and observe all the rules below.
- Do not reverse the battery cable connections. This will burn out the diodes on the electrical parts.
- Always check battery condition before condemning other parts of an electrical system. A fully charged battery is a must for conducting accurate electrical system tests.
- The electrical parts should never be struck sharply, as with a hammer, or allowed to fall on a hard surface. Such a shock to the parts can damage them.
- To prevent damage to electrical parts, do not disconnect the battery cables or any other electrical connections when the ignition switch is ON, or while the engine is running.
- Because of the large amount of current, never keep the starter button pushed when the starter motor will not turn over, or the current may burn out the starter motor windings.
- Take care not to short the cables that are directly connected to the battery positive (+) terminal to the chassis ground.
- Troubles may involve one or in some cases all items.
Never replace a defective part without determining what CAUSED the failure. If the failure was caused by some other item or items, they must be repaired or replaced, or the new replacement will soon fail again.
- Make sure all connectors in the circuit are clean and tight, and examine wires for signs of burning, fraying, etc. Poor wires and bad connections will affect electrical system operation.
- Measure coil and winding resistance when the part is cold (at room temperature).
Electrical Wiring
Wiring Inspection
- Visually inspect the wiring for signs of burning, fraying, etc.
If any wiring is poor, replace the damaged wiring.
- Pull each connector [A] apart and inspect it for corrosion, dirt, and
damage.
If the connector is corroded or dirty, clean it carefully. If it is damaged, replace it.
- Check the wiring for continuity.
- Use the wiring diagram to find the ends of the lead which is suspected of being a problem.
- Connect the hand tester between the ends of the leads.
Special Tool - Hand Tester: 57001-1394

- Set the tester to the × 1 Ω range, and read the tester.
If the tester does not read 0 Ω, the lead is defective. Replace the lead or the wiring harness [B] if necessary.


 Rider's Manual BMW R 1250 GS GSA
Rider's Manual BMW R 1250 GS GSA Owner's Manual Harley-Davidson Sportster XL1200X Forty-Eight
Owner's Manual Harley-Davidson Sportster XL1200X Forty-Eight Owner's Manual Honda CBR650R
Owner's Manual Honda CBR650R Service manual Honda CBR650
Service manual Honda CBR650 Owner's Manual Honda PCX125
Owner's Manual Honda PCX125 Owner's Manual Kawasaki Z1000SX
Owner's Manual Kawasaki Z1000SX Service manual Kawasaki Z1000SX
Service manual Kawasaki Z1000SX Owner's Manual Lexmoto Echo
Owner's Manual Lexmoto Echo Owner's Manual Royal Enfield Interceptor 650
Owner's Manual Royal Enfield Interceptor 650 Service manual Royal Enfield Interceptor 650
Service manual Royal Enfield Interceptor 650 Owner's Manual Yamaha MT-07
Owner's Manual Yamaha MT-07